Eligibility & the Process for Employment Insurance
Employment Insurance or EI in Canada is a system made to provide monetary benefits to those who lose their jobs as long as there hold no fault of their own. Some examples are shortages of work, seasonal and mass lay-offs. The individuals are able to and available for work but can’t find a job at the time.
As soon as you stop working, apply for Employment Insurance (EI) even if you have not received your Record of Employment (ROE). Delaying your claim for more than four weeks after your last day of work results in a possible loss of benefits. The Record of Employment or ROE is a document provided by your employer that proves your work history with them up until termination.
Qualifying for Employment Insurance
When submitting your EI claim, the following needs to be proven:
- You were employed in insurable employment.
- Losing the job was not due to your own fault.
- Employment was affected by flooding or wildfires.
- Have not worked and did not receive pay for 7 days straight in the last 52 weeks.
- Your hours worked since the last EI claim or the last 52 weeks meet the required number of insurable employment hours in your region.
- You are willing, ready and capable of working every day.
- Finally, you should be actively looking for work, recording employers contacted and when you contacted them.
While on Employment Insurance, you are expected to consistently prove your eligibility to receive payments by completing bi-weekly reports. This can be done online or by the phone but missing these reports can result in losing your benefits.
You Do Not Qualify for EI if You:
- You voluntarily left your job without just cause.
- Dismissal for misconduct.
- Participation in a labour dispute caused unemployment.
- This includes strikes, lockouts and other conflicts.
- If this is a period of elave that compensates for a period which you worked more hours than normal in full-time employment and have an agreement with your employer.
- Quitting or losing your job due to non-compliance with the employer’s mandatory COVID-19 vaccination policy.
- The employer must have clearly communicated the policy.
- Informed you that not complying would result in loss of employment.
- If applying the policy was reasonable within the workplace context.
- You have a valid reason for not complying and didn’t receive an exemption from your employer.
- You’re in jail and are found guilty by a court of law.
- If you are incarcerated and were not found guilty, you may receive an extension in the qualifying and benefit period for your EI payments.
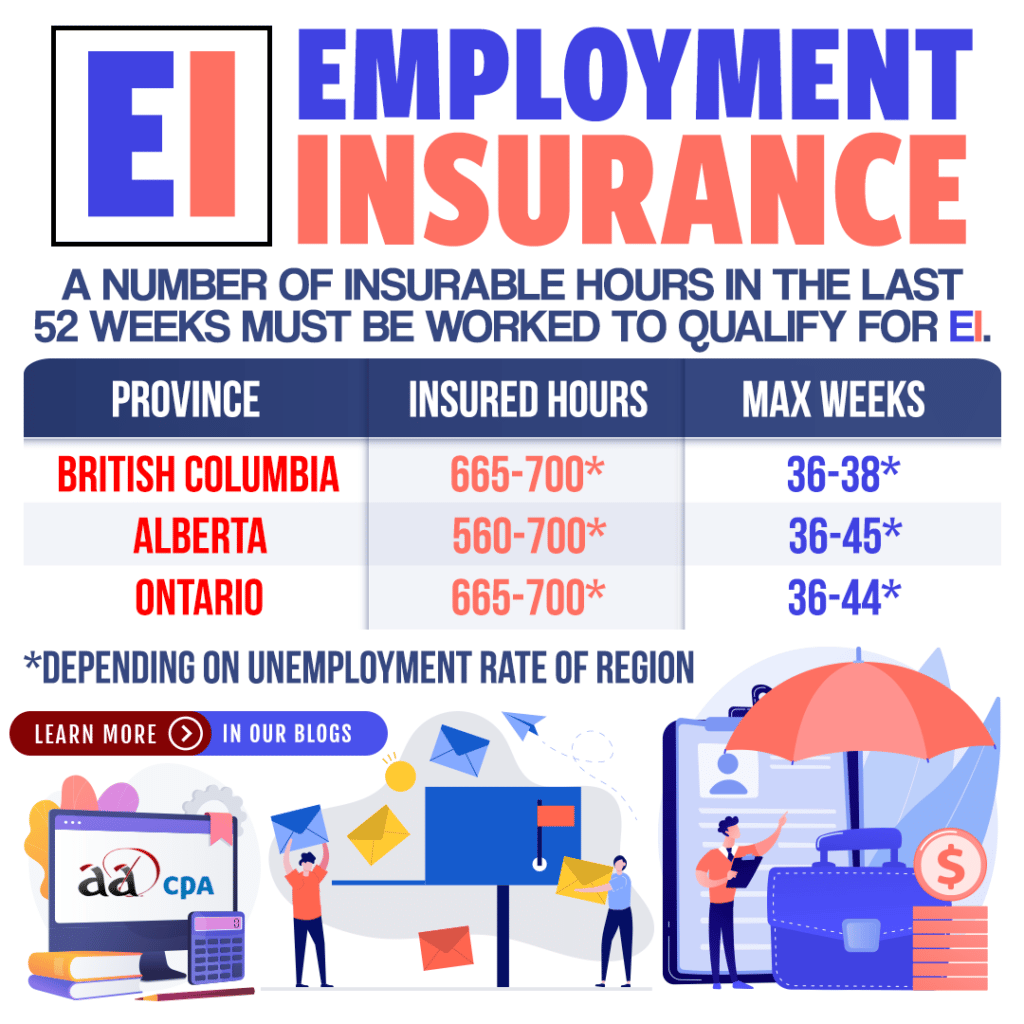
Insurable Hours & Maximum Weeks for EI
To qualify for EI, there is a qualifying period that requires a number of hours in insurable employment. This period is the shorter of these two options:
- 52-week period immediately before the start date of the EI claim.
- Period from the start of a previous EI benefit period to the start of the new benefit period.
- This is if you applied for benefits earlier and your application was approved in the last 52 weeks.
Depending on the rate of unemployment in your region, the insured hours required range from 420 – 700 and the maximum weeks of benefits ranges from 36 – 45.
Depending on the rate of unemployment in your region, the insured hours required range from 420 – 700 and the maximum weeks of benefits ranges from 36 – 45.
Find out more by reviewing the CRA’s section on their website discussing Employment Insurance here.
Alternatively, to find out the unemployment rate in your region and the number of hours required to qualify for benefits, click here to look up your EI economic region by postal code.