Guide to Tax on Crypto Gains in Canada
Cryptocurrency is becoming a more common investment tool day-by-day, with coins like Bitcoin and Ethereum leading the way. Other crypto assets are making their way into regular dealings for investors as well, but there are taxes to consider on crypto gains. When dealing in crypto assets, you need to understand the tax implications that come with their income and profits. Read our guide below to understand the tax obligations crypto investors and businesses face in Canada.
Types of Crypto-Assets Leading to Crypto Gains
Crypto-Assets
Crypto assets are any digital assets that are on a cryptographically secured distributed ledger. While there are many types of crypto assets, the most used ones are cryptocurrencies (fungible tokens) and NFTs (non-fungible tokens). Crypto-asset exchanges are online platforms for users to buy, sell, and trade crypto-assets. Lending and staking arrangements occur on these platforms as well, while servicing Canadians from around the world.
Cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrency is a type of virtual asset protected using cryptography and often recorded on a blockchain. It operates independently of traditional financial institutions but still has a history of transactions recorded. Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum, Tether, and other crypto coins are independent and are not backed by governments, central banks, or other authorities.
Cryptocurrencies change in value due to supply and demand. They are traded through exchanges and held in digital wallets. While cryptocurrencies offer opportunities for investment and financial transactions, they come with tax obligations that investors need to consider and comply with.
Crypto Transactions and Crypto Gain Tax Implications
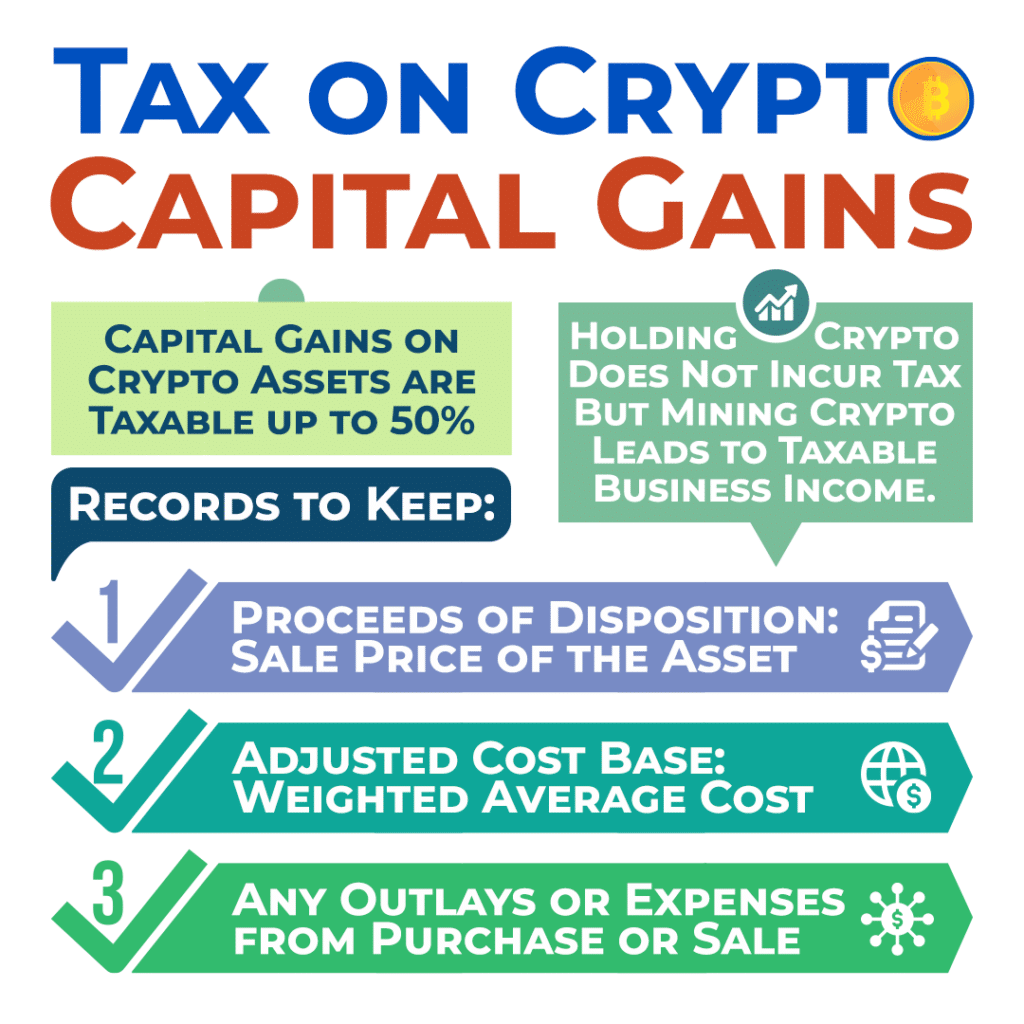
In general, just holding cryptocurrencies does not result in any taxes. Crypto transactions can result in either capital gains or business income, depending on the nature of the activity. Capital gains are incurred when disposing of cryptocurrency, such as selling, trading, or using it to purchase goods or services. On the other hand, if crypto activities are considered part of a business, the profits are classified as business income.
Capital Gains Tax Treatment of Crypto Gains
When selling, trading, gifting, converting, or exchanging any cryptocurrency, you need to make sure you have records of the following:
- Proceeds of the disposition.
- Sale Price of the Crypto Asset
- Adjusted cost base.
- Weighted Average Cost of a Crypto Asset
- Outlays and expenses incurred.
If you sell a cryptocurrency for more than the original purchase price or adjusted cost base, it results in a capital gain. Make sure to keep track of how the fair market value of the crypto asset was calculated in case of a CRA review or audit. Fifty percent of capital gains are taxable income and must be reported on the tax return using T1 Schedule 3 – Capital Gains (or Losses).
Valuation of Cryptocurrency
Determining the value of cryptocurrency is key to report your capital gains or losses accurately. Whether classified as capital property or inventory, investors must track acquisition costs and fair market values to calculate capital gains or business income accurately. If it’s considered capital property, the cost from acquiring it is used to evaluate the value. If the cryptocurrency is inventory, the valuation is based on:
- Cost of each item when it was obtained.
- Fair market value at year-end.
Capital Losses on Crypto
Half of your capital losses or your allowable capital losses can be deducted from your taxable capital gains. It can’t be deducted from other sources of income like employment. If you were scammed when dealing in crypto assets, you can claim a loss. In this case, it’s especially recommended to work with a tax professional to find out more information.
Not Sure How to Report Crypto Gains or Losses?
Get help from a tax expert today, in time for your tax return filing.
Tax Treatment of Crypto Business Income
For investors in crypto-related businesses such as mining or trading as a primary source of income, profits are business income. Business activities need to be reported on their tax returns, and expenses incurred in conducting the business may be deductible.
Crypto in Goods and Services
If a taxable property or service is exchanged for cryptocurrency, GST/HST still needs to be considered. To calculate the GST/HST on the transaction, use the fair market value of the cryptocurrency when the exchange occurred.
Tax Implications of Mining
Cryptocurrency miners’ group valid transactions into blocks. When these blocks are accepted by the cryptocurrencies network, they become part of the blockchain’s public ledger. This is done through computers and specialized hardware and can have tax implications.
Payments occur through income in the form of the cryptocurrency from the creation of a new cryptocurrency and successful validation. Tax treatment depends on whether it’s considered a hobby or business activity. Income from mining is taxable, while associated expenses can be deductible for businesses. In addition, any capital gains from selling the newly validated cryptocurrency are taxable.
Reporting Requirements on Crypto Gains
To meet tax obligations, investors need to keep accurate records of all crypto activities, including purchases, sales, and mining. This is because capital gains, losses, or business income leads to an impact on taxes owed. Make sure you have accurate information about any of your activities on crypto-asset exchanges. Because exchanges can stop operating without notice, locking account holders out, it is crucial to download and keep information on transactions related to exchange accounts as they happen. Activities to keep records for include:
- Trades
- Anytime you buy, sell, or swap on the crypto exchange.
- Transfers
- Anytime you deposit or withdraw from the exchange.
- Staking Rewards
- Yield Earnings
- Wallet Addresses
- All other transaction information.
The information on crypto asset activities should include details such as:
- Number and Type of Units
- Transaction Dates and Times
- Transaction ID
- Receipts for Purchase or Transfer
- Amounts and Values in Canadian Dollars
- Descriptions of Transactions and the Other Party
- Addresses for the Digital Wallets Used
- General Wallet and Exchange Records
- Beginning and Ending Wallet Balances and Costs
- This is for each crypto asset annually.
- Accounting and Legal Costs
- Software Costs for Managing Taxes
- Costs Specific to Cryptocurrency Miners:
- Receipts for buying mining hardware.
- Receipts for expenses that support mining.
- Contracts and records for the mining pool.
- Anything else related to mining activities.
- Disposal costs of cryptocurrency earned from mining.
Failing to maintain proper records results in challenges during tax filing and potential audits by the Canada Revenue Agency (CRA).
Filing Deadlines and Penalties
The deadline for most Canadian tax return filing and payments is on April 30, unless you or your spouse are self-employed or have business income. In that case, the deadline to file is on June 15 but the payment due date is still on April 30. Keeping these dates in mind, make sure your crypto transaction records are accurate much before the deadlines to avoid delays to your tax filing. Late returns and payments lead to penalties and interest, and not reporting crypto income or capital gains can cause audits as well.
Avoiding and Reducing Penalties
If you are in the situation where your income or capital crypto gains were not reported in previous tax returns, you can still get ahead of any issues with the CRA by:
- Changing your income tax and benefit return by refiling it.
- Adjusting your GST/HST return.
- Applying for a correction using the Voluntary Disclosures Program.
Working with a Professional on Crypto Gains
Because the taxation of crypto assets is complex and needs detailed records from relevant places, it is recommended that investors talk to a tax professional. Qualified CPA accounting firms specializing in tax are the perfect fit for these sophisticated investors. They’ll help you with tax planning, record-keeping, return filing, and compliance with CRA regulations. At Advanced Tax we provide expert services for tax, bookkeeping, and accounting needs. Our highly qualified team understands your unique needs, especially when dealing in crypto gains from crypto assets. Contact us today to learn more about how we can make it easy for you to comply with the CRA regarding your crypto investments and businesses.